Assume your company’s standard cost for denim is $3 per yard, but you buy some denim at a bargain price of $2.50 per yard. For each yard of denim purchased, DenimWorks reports a favorable direct materials price variance of $0.50. These thin margins are the reason autosuppliers examine direct materials variances so carefully. Anyunexpected increase in steel prices will likely cause significantunfavorable materials price variances, which will lead to lowerprofits.
Ask Any Financial Question
Forauto suppliers that use hundreds of tons of steel each year, thishad the unexpected effect of increasing expenses and reducingprofits. For example, a major producer of automotive wheels had toreduce its annual earnings forecast by $10,000,000 to $15,000,000as a result of the increase in steel prices. Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University. He has taught accounting at the college level for 17 years and runs the Accountinator website at , which gives practical accounting advice to entrepreneurs. We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Relationship Between Variances
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
What Is Unfavorable Variance?
This concept involves examining the differences between expected and actual costs of materials used in production, providing insights into potential areas for financial improvement. A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials. An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, indicates that the amount of materials used exceeds the standard requirement. The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency.
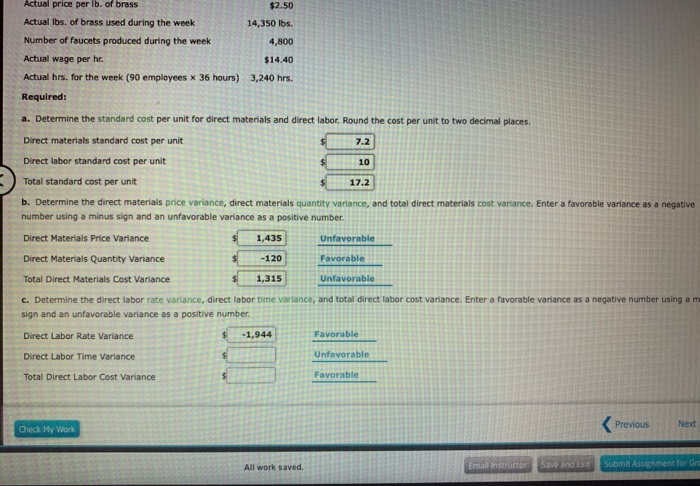
Formulas to Calculate Material Cost Variance and Material Price Variance
The amount of materials used and the price paid for those materials may differ from the standard costs determined at the beginning of a period. A company can compute these materials variances and, from these calculations, can interpret the results and decide how to address these differences. Direct material price variance (DM Price Variance) is defined as the difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials. It evaluates the extent to which the standard price has been over or under applied to different units of purchase.
This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35. As you calculate variances, youshould think through the variance to confirm whether it isfavorable or unfavorable. A favorable direct material yield variance means a higher production than the standard or expected production based on the standard input quantities of materials. An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, means lower production than the standard production based on standard input quantity.
This is a favorable outcome because the actual price for materials was less than the standard price. The difference column shows that 200 fewer pounds were used than expected (favorable). It also shows that the actual price per pound was $0.30 higher than standard cost (unfavorable). The direct materials used in production cost more than was anticipated, which is an unfavorable outcome. If the actual quantity of materials used is less than the standard quantity used at the actual production output level, the variance will be a favorable variance.
- Premium Furniture, a US based Inc., uses a standard costing system to control its direct materials and conversion costs.
- To calculate a budget variance, go through each line item in your budget and subtract the actual spend from the original budget.
- As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider using cheaper materials, changing suppliers, or increasing prices to cover costs.
Based on production and sales being equal at 1,620 units, the total standard cost would have been $38,880. The same calculation is shown using the outcomes of the direct materials price and quantity variances. how to fill out and file form w To apply this method to the Band Book example, take a look at the next diagram. Direct materials actually cost $297,000, even though the standard cost of the direct materials is only $289,800.
In other words, when actual quantity of materials used deviates from the standard quantity of materials allowed to manufacture a certain number of units, materials quantity variance occurs. With either of these formulas, the actual quantity purchased refers to the actual amount of materials bought during the period. If there is no difference between the standard price and the actual price paid, the outcome will be zero, and no price variance exists. If the actual price paid per unit of material is lower than the standard price per unit, the variance will be a favorable variance. A favorable outcome means you spent less on the purchase of materials than you anticipated. If, however, the actual price paid per unit of material is greater than the standard price per unit, the variance will be unfavorable.
Generally, the production managers are considered responsible for direct materials quantity variance because they are the persons responsible for keeping a check on excessive usage of production inputs. However, purchase managers may purchase low quality, substandard or otherwise unfit materials with an intention to improve direct materials price variance. In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department.
